What to do if you have trouble swallowing rice -dysphagia – Experiencing difficulty swallowing rice? You may be experiencing dysphagia, a condition that affects the swallowing process. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is crucial. Join us as we explore what to do if you have trouble swallowing rice and empower you with the knowledge to manage this condition effectively.
Definition and Overview of Dysphagia: What To Do If You Have Trouble Swallowing Rice -dysphagia
Dysphagia, also known as difficulty swallowing, is a medical condition that affects the ability to move food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Neurological disorders, such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis
- Structural abnormalities in the mouth, throat, or esophagus
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Tumors or other growths in the digestive tract
Dysphagia can be classified into two main types:
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
Oropharyngeal dysphagia affects the muscles and nerves involved in swallowing in the mouth and throat. It can cause difficulty initiating swallowing, holding food in the mouth, or moving food from the mouth to the throat.
Esophageal Dysphagia
Esophageal dysphagia affects the muscles and nerves involved in swallowing in the esophagus. It can cause difficulty moving food from the throat to the stomach, resulting in a feeling of food getting stuck in the chest.
Causes and Risk Factors of Dysphagia
Dysphagia can result from various underlying medical conditions and lifestyle habits. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Neurological disorders, such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis, can affect the nerves and muscles involved in swallowing. Esophageal strictures, narrowings of the esophagus, can also obstruct the passage of food and liquids. Zenker’s diverticulum, a pouch-like protrusion in the upper esophagus, can trap food and cause swallowing difficulties.
Lifestyle Factors and Habits
Smoking damages the esophageal lining, increasing the risk of inflammation and scarring. Alcohol consumption can impair the function of the muscles involved in swallowing. Poor dental hygiene can lead to dental problems that affect chewing and swallowing, such as tooth decay and gum disease.
If you’re having trouble swallowing rice – a condition known as dysphagia – it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause. While waiting for your appointment, you may find relief from throat pain by following the tips provided in this article: Que puede tomar una embarazada para el dolor de garganta . Remember, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for dysphagia.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Dysphagia
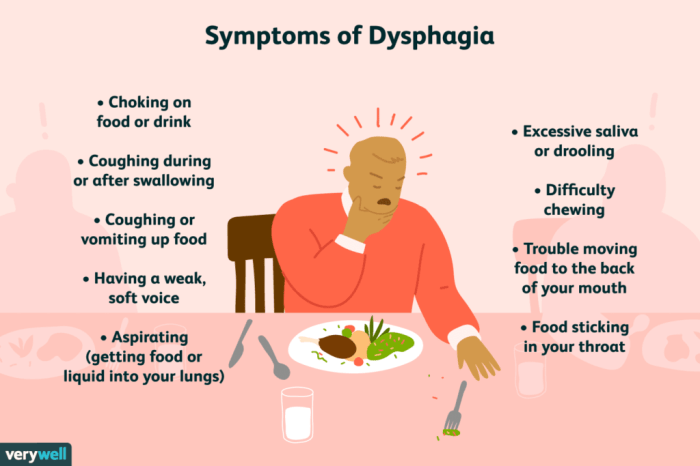
Dysphagia can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild discomfort to severe swallowing difficulties. It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms and seek medical attention if you suspect you may have dysphagia.
The common symptoms of dysphagia include:
- Difficulty swallowing food or liquids
- Pain or discomfort during swallowing
- Regurgitation of food or liquids into the mouth or nose
To confirm a diagnosis of dysphagia, healthcare professionals typically conduct diagnostic procedures such as:
Barium Swallow Studies
A barium swallow study involves consuming a liquid containing barium, a contrast agent that coats the esophagus and makes it visible on X-rays. This procedure helps identify any structural abnormalities or blockages in the esophagus.
Endoscopy
During an endoscopy, a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to visualize the lining and identify any abnormalities, such as inflammation, ulcers, or tumors.
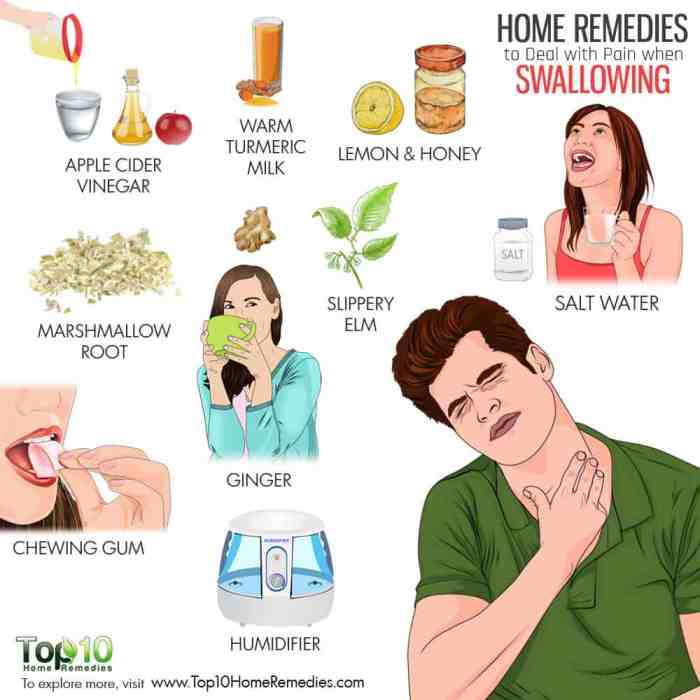
If you’re having trouble swallowing rice, it’s important to see a doctor to rule out any underlying medical conditions. While you’re waiting for your appointment, you can try some home remedies to ease the discomfort. One thing you can try is gargling with salt water.
Another option is to suck on a hard candy or lozenge. If these methods don’t provide relief, you may want to consider talking to your doctor about egg donation . Egg donation is a great way to help infertile couples have children.
It’s also a relatively simple procedure that can be completed in a few weeks. If you’re interested in learning more about egg donation, be sure to talk to your doctor.
Manometry
Manometry measures the pressure and coordination of the muscles in the esophagus during swallowing. It can detect any abnormalities in the muscle function that may contribute to dysphagia.
Treatment Options for Dysphagia
Managing dysphagia involves a multidisciplinary approach that may include dietary modifications, swallowing exercises, medications, and in some cases, surgery.
The specific treatment plan will depend on the underlying cause and severity of dysphagia.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary modifications are often the first line of treatment for dysphagia. These modifications may include:
- Changing the texture of foods to make them easier to swallow, such as pureeing or mashing foods.
- Avoiding certain foods that are difficult to swallow, such as sticky or chewy foods.
- Eating smaller bites and chewing thoroughly.
- Drinking plenty of fluids to help lubricate the throat and esophagus.
Swallowing Exercises
Swallowing exercises can help strengthen the muscles involved in swallowing and improve coordination. These exercises may include:
- Tongue exercises, such as sticking out the tongue and moving it around.
- Jaw exercises, such as opening and closing the jaw slowly.
- Throat exercises, such as gargling or humming.
Medications
Medications may be used to treat dysphagia caused by certain medical conditions, such as acid reflux or muscle weakness. These medications may include:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce stomach acid.
- Muscle relaxants to relax the muscles in the esophagus.
- Anticholinergics to reduce saliva production.
Surgery
Surgery may be necessary to treat dysphagia if other treatments have not been successful. Surgical procedures may include:
- Esophageal dilation to widen the esophagus.
- Stenting to place a tube in the esophagus to keep it open.
- Esophagectomy to remove part of the esophagus.
Complications of Dysphagia
Dysphagia can lead to several complications if not diagnosed and treated promptly. These complications can significantly impact a person’s health and well-being.
Malnutrition
Difficulty swallowing can make it challenging for individuals to consume adequate amounts of food and nutrients. Over time, this can lead to malnutrition, characterized by a deficiency in essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Malnutrition can weaken the immune system, impair cognitive function, and increase the risk of infections and other health problems.
Dehydration
Dysphagia can also cause dehydration, as individuals may avoid drinking fluids due to the discomfort or pain associated with swallowing. Dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances, fatigue, confusion, and, in severe cases, kidney damage.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a serious complication of dysphagia that occurs when food or liquid enters the lungs during swallowing. This can lead to inflammation and infection in the lungs, potentially resulting in severe respiratory problems and even death.
Importance of Timely Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of dysphagia are crucial to prevent these complications. Seeking medical attention if you experience difficulty swallowing is essential. Treatment options may include dietary modifications, swallowing exercises, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Timely intervention can help improve swallowing function, reduce the risk of complications, and maintain overall health and well-being.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Modifications
Managing dysphagia can be improved with certain home remedies and lifestyle modifications. These include:
Eating Smaller Meals
Consuming smaller meals can reduce the amount of food that needs to be swallowed at once, making it easier to manage. It is recommended to eat frequent, small meals throughout the day rather than large ones.
Avoiding Certain Foods
Certain foods can be more difficult to swallow than others. Avoiding foods that are hard, sticky, or chewy can help reduce the risk of choking or aspiration. Some examples of foods to avoid include raw vegetables, tough meats, and sticky candies.
Maintaining Good Posture
Maintaining good posture while eating and drinking can help improve swallowing. Sitting up straight with your head slightly tilted forward can help keep your airway open and make swallowing easier.
Seeking Professional Advice
It is important to seek professional advice before implementing any home remedies or lifestyle modifications for dysphagia. A speech-language pathologist or other healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and support based on your specific needs.
Prevention of Dysphagia
Taking proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing dysphagia. Maintaining good oral hygiene, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding potential risk factors are crucial in preventing this condition.
Regular medical checkups are essential for early detection and intervention, as timely diagnosis and treatment can prevent the progression of dysphagia and improve outcomes.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
Practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as brushing twice daily, flossing regularly, and using mouthwash, can help prevent gum disease, tooth decay, and oral infections. These conditions can contribute to dysphagia by causing pain, swelling, and difficulty chewing and swallowing.
Managing Underlying Medical Conditions
Underlying medical conditions, such as neurological disorders, stroke, and certain cancers, can increase the risk of dysphagia. Managing these conditions effectively, through medication, therapy, or lifestyle modifications, can help prevent or reduce the severity of dysphagia.
Avoiding Risk Factors
Certain risk factors, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and head and neck injuries, can contribute to dysphagia. Avoiding these risk factors can help reduce the likelihood of developing this condition.
Impact on Quality of Life

Dysphagia can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, affecting both physical and emotional well-being.
Social isolation is a common consequence of dysphagia. Difficulty eating and swallowing can make it challenging to participate in social events, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Emotional Impact, What to do if you have trouble swallowing rice -dysphagia
Dysphagia can also lead to depression and anxiety. The frustration and embarrassment associated with swallowing difficulties can contribute to low self-esteem and a negative body image. Additionally, the fear of choking or malnutrition can cause significant anxiety.
If you’re struggling with swallowing rice, known as dysphagia, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. While it may not seem like a serious issue, dysphagia can be a sign of an underlying medical condition. In some cases, such as blood in urine after radiation treatment for prostate cancer , it’s essential to address the root cause promptly to prevent further complications.
So, if you’re experiencing difficulty swallowing, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Importance of Emotional Support
Emotional support and counseling are crucial for individuals with dysphagia. Therapists can provide coping mechanisms, address emotional challenges, and improve self-esteem. Support groups can also offer a sense of community and understanding, reducing feelings of isolation.
Resources and Support Groups
Individuals with dysphagia and their caregivers can benefit from connecting with others who understand the challenges of this condition. Support groups provide a platform for sharing experiences, offering emotional support, and exchanging practical advice.
Joining a support group can provide several benefits, including:
- Emotional support and validation from others who understand the challenges of dysphagia
- Practical advice and tips on managing dysphagia
- Information about resources and services available to individuals with dysphagia
- A sense of community and belonging
National Organizations
- National Foundation of Swallowing Disorders (NFOSD): Provides information, support, and resources for individuals with swallowing disorders and their caregivers.
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA): Offers a directory of speech-language pathologists who specialize in swallowing disorders.
Local Support Groups
Many communities have local support groups for individuals with dysphagia. These groups can be found through local hospitals, rehabilitation centers, or community organizations.
Outcome Summary
Managing dysphagia requires a multifaceted approach involving medical interventions, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Seek professional guidance, connect with support groups, and embrace a positive mindset. With the right strategies, you can overcome the challenges of dysphagia and regain a fulfilling quality of life.
Query Resolution
What are the common causes of dysphagia?
Dysphagia can result from various underlying medical conditions, including neurological disorders, esophageal strictures, and Zenker’s diverticulum.
What are the symptoms of dysphagia?
Difficulty swallowing, pain or discomfort during swallowing, and regurgitation are common symptoms of dysphagia.
How is dysphagia diagnosed?
Barium swallow studies, endoscopy, and manometry are diagnostic procedures used to confirm dysphagia.
What are the treatment options for dysphagia?
Treatment options include dietary modifications, swallowing exercises, medications, and, in severe cases, surgery.
How can I prevent dysphagia?
Maintaining good oral hygiene, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding risk factors can help reduce the risk of developing dysphagia.