As how do i get 300 grams of protein a day takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Delving into the nutritional intricacies of protein, we embark on a journey to unravel the secrets of meeting your daily protein requirements.
Protein, the building block of life, plays a pivotal role in various bodily functions. From muscle growth and repair to hormone production and immune system support, protein is essential for optimal health and well-being. Understanding how to incorporate 300 grams of protein into your daily diet can empower you to unlock its full potential.
Nutritional Value of Protein
Protein is a vital nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It is essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. Protein also helps regulate fluid balance and maintain blood sugar levels.
Different protein sources provide varying amounts of essential amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. A balanced diet should include a variety of protein sources to ensure adequate intake of all essential amino acids.
Nutritional Value of Different Protein Sources
The table below summarizes the nutritional value of different protein sources per 100 grams:
| Protein Source | Protein (g) | Calories | Fat (g) | Carbohydrates (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken breast (cooked) | 27 | 165 | 3 | 0 |
| Beef (lean, cooked) | 26 | 250 | 15 | 0 |
| Fish (salmon, cooked) | 25 | 200 | 12 | 0 |
| Eggs | 13 | 155 | 11 | 1 |
| Beans (black, cooked) | 15 | 130 | 1 | 20 |
| Tofu | 8 | 70 | 4 | 2 |
Dietary Sources of Protein
Protein is a crucial macronutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. To meet the recommended daily intake of 300 grams of protein, it is essential to incorporate protein-rich foods into your diet. This section will explore common dietary sources of protein, categorized into animal-based and plant-based options, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Animal-Based Protein Sources, How do i get 300 grams of protein a day
Animal-based protein sources are typically complete proteins, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids. They are generally considered to be more bioavailable than plant-based proteins, meaning they are more easily absorbed and utilized by the body.
- Meat:Red meat (beef, pork, lamb), poultry (chicken, turkey), and fish are excellent sources of protein. They provide high-quality protein with a good balance of amino acids.
- Dairy products:Milk, cheese, and yogurt are rich in protein and calcium. They are a good choice for individuals who are lactose-tolerant.
- Eggs:Eggs are a versatile source of protein that is complete and contains essential nutrients like choline and vitamin D.
Advantages:Animal-based proteins are complete proteins and are highly bioavailable. They are a good source of essential amino acids and provide other nutrients like iron and vitamin B12.
Disadvantages:Animal-based proteins can be higher in saturated fat and cholesterol compared to plant-based proteins. They may also be more expensive and have ethical concerns associated with animal agriculture.
Plant-Based Protein Sources
Plant-based protein sources are incomplete proteins, meaning they do not contain all nine essential amino acids. However, by combining different plant-based proteins, it is possible to obtain a complete amino acid profile.
- Legumes:Beans (black beans, kidney beans), lentils, and peas are excellent sources of protein and fiber. They are also a good source of iron and folate.
- Soy products:Tofu, tempeh, and edamame are made from soybeans and are complete proteins. They are a good alternative to animal-based proteins for vegans and vegetarians.
- Nuts and seeds:Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flax seeds are good sources of protein and healthy fats. They can be incorporated into smoothies, salads, and trail mixes.
- Whole grains:Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats contain protein and fiber. They can be a good addition to a balanced diet.
Advantages:Plant-based proteins are generally lower in saturated fat and cholesterol compared to animal-based proteins. They are also a good source of fiber and other nutrients like antioxidants and phytochemicals. Additionally, plant-based diets are associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases.
Getting 300 grams of protein daily can be a challenge, but it’s crucial for maintaining muscle mass and supporting overall health. If you’ve undergone gastric bypass and are struggling to lose weight, you may be wondering why. This article explores the potential reasons behind this issue and offers guidance on addressing them.
Regardless of your weight loss journey, meeting your protein requirements remains essential for optimal health.
Disadvantages:Plant-based proteins are incomplete proteins and require combining different sources to obtain a complete amino acid profile. They may also be lower in certain nutrients like iron and vitamin B12, which need to be supplemented or obtained from fortified foods.
Planning a High-Protein Diet
Planning a high-protein diet requires careful calculation and thoughtful meal planning. This section provides guidance on how to determine your daily protein requirements, incorporate more protein into your meals, and create a sample meal plan that meets your target of 300 grams of protein per day.
Calculating Daily Protein Requirements
The recommended daily protein intake varies based on individual factors such as age, weight, activity level, and health goals. A general guideline is to consume 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. For example, if you weigh 75 kilograms, you should aim for 60 grams of protein per day.
However, if you are highly active or seeking muscle growth, you may need more protein. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine your personalized protein needs.
Incorporating More Protein into Meals
Incorporating more protein into your meals can be achieved through various strategies. Consider the following tips:
- Choose lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, beans, lentils, and tofu.
- Add protein powder to smoothies, shakes, or oatmeal.
- Snack on high-protein foods like nuts, seeds, and Greek yogurt.
- Include a protein source at every meal, even breakfast.
- Experiment with new protein-rich recipes and cuisines.
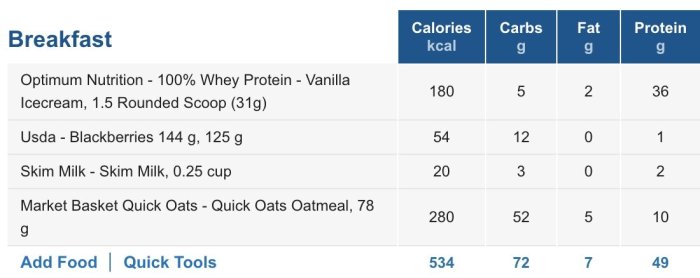
Sample Meal Plan with 300 Grams of Protein per Day
Here is a sample meal plan that provides approximately 300 grams of protein per day:
| Meal | Protein Source | Serving Size | Protein Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Eggs | 4 large | 56 grams |
| Snack | Greek Yogurt | 1 cup | 24 grams |
| Lunch | Grilled Chicken Salad | 1 cup | 50 grams |
| Snack | Protein Shake | 1 scoop | 25 grams |
| Dinner | Salmon with Roasted Vegetables | 6 ounces | 50 grams |
| Snack | Casein Protein Pudding | 1 cup | 25 grams |
| Total | 230 grams |
Note: This is just a sample meal plan, and you may need to adjust it based on your individual needs and preferences. Ensure you consume a variety of protein sources throughout the day to meet your protein target and support overall health.
Protein Supplements

Protein supplements are convenient and effective ways to increase your protein intake. They come in various forms, including powders, bars, and shakes, and can be easily incorporated into your diet. Supplements can help you meet your protein goals, especially if you have a busy lifestyle or find it challenging to consume enough protein from whole food sources alone.
Types of Protein Supplements
*
-*Whey Protein
Derived from milk, whey protein is a fast-digesting protein that is quickly absorbed by the body. It is a rich source of essential amino acids, making it ideal for muscle growth and recovery.
-
-*Casein Protein
Also from milk, casein protein is a slow-digesting protein that provides a sustained release of amino acids over several hours. It is often used before bedtime to support muscle recovery during sleep.
-*Soy Protein
A plant-based protein, soy protein is a complete protein containing all essential amino acids. It is a good option for vegans and vegetarians and has additional health benefits, such as reducing cholesterol levels.
-*Pea Protein
Another plant-based protein, pea protein is a hypoallergenic and easily digestible option. It is rich in iron and fiber and is a good choice for individuals with allergies or sensitivities.
Guidelines for Safe and Effective Use
*
-*Choose high-quality supplements
Consuming 300 grams of protein daily can be challenging, but balancing protein sources with a focus on gut health is essential. One common concern for women is the impact of birth control on gut health. If you’re looking for ways to heal your gut while on birth control, check out this article . It provides practical tips and insights into supporting your gut microbiome.
By understanding the link between gut health and protein intake, you can make informed choices to meet your daily protein goals while maintaining a healthy digestive system.
Look for supplements that are third-party tested and certified to ensure purity and quality.
-
-*Determine your protein needs
Calculate your daily protein requirements based on your weight, activity level, and fitness goals.
-*Use supplements as a supplement
To get 300 grams of protein daily, consider consulting with a registered dietitian or exploring how much it costs to fix Peyronie’s disease if you’re experiencing discomfort. Protein-rich foods like lean meats, fish, and legumes can aid in achieving your protein goals while maintaining a healthy diet.
Protein supplements should not replace whole food sources of protein. Aim to consume the majority of your protein from healthy food choices.
-*Consider your allergies and sensitivities
If you have any allergies or sensitivities, carefully check the ingredient list of protein supplements to avoid potential reactions.
-*Follow recommended dosages
Do not exceed the recommended dosages on the supplement label. Excessive protein intake can have adverse effects on your health.
Protein Absorption and Metabolism
Protein absorption and metabolism are crucial processes that ensure the body utilizes protein effectively. Understanding these processes can help optimize protein intake and support overall health.
Protein digestion begins in the stomach, where stomach acid and enzymes break down proteins into smaller peptides. These peptides then travel to the small intestine, where further digestion occurs through the action of pancreatic enzymes and enzymes secreted by the intestinal lining.
The resulting amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream through the walls of the small intestine.
Factors Affecting Protein Absorption and Metabolism
Several factors can influence protein absorption and metabolism, including:
- Protein source:Animal proteins are generally more easily absorbed than plant proteins.
- Protein quality:The amino acid composition and digestibility of the protein affect its absorption.
- Stomach pH:Low stomach pH can hinder protein digestion.
- Intestinal health:Conditions that impair intestinal function can affect protein absorption.
- Age:Protein absorption may decline with age.
Tips for Maximizing Protein Utilization
To maximize protein utilization, consider the following tips:
- Consume a variety of protein sources:Include both animal and plant proteins to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
- Choose high-quality protein:Opt for proteins with high digestibility and essential amino acid content.
- Maintain optimal stomach pH:Avoid acidic foods and beverages before protein consumption.
- Support intestinal health:Consume probiotics, fiber, and fermented foods to promote a healthy digestive system.
- Consider protein timing:Spread protein intake throughout the day to enhance muscle protein synthesis.
Health Benefits of Consuming 300 Grams of Protein Daily
Consuming 300 grams of protein daily can provide numerous health benefits, including enhanced muscle growth, weight loss, and overall well-being. Scientific studies have demonstrated the positive impact of a high-protein diet on various aspects of health.
Muscle Growth and Strength
Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair. Consuming adequate protein helps stimulate muscle protein synthesis, the process by which new muscle tissue is formed. Studies have shown that individuals who consume higher amounts of protein experience greater gains in muscle mass and strength compared to those who consume lower amounts.
Weight Loss and Maintenance
A high-protein diet can promote weight loss and maintenance by increasing satiety, reducing hunger, and boosting metabolism. Protein takes longer to digest than carbohydrates or fats, which helps you feel fuller for longer periods. Additionally, protein has a higher thermic effect than other macronutrients, meaning it requires more energy to digest and utilize.
Overall Health
Consuming adequate protein is crucial for overall health. Protein is involved in various bodily functions, including immune system regulation, hormone production, and tissue repair. A high-protein diet has been linked to improved immune function, reduced risk of chronic diseases, and better cognitive performance.
Risks and Considerations
Consuming excessive protein can pose certain risks. Excessive protein intake can put a strain on the kidneys, as they work harder to filter out the waste products produced during protein metabolism. Additionally, a high-protein diet can lead to dehydration if adequate fluid intake is not maintained.It
is important to balance protein intake with other nutrients to ensure a healthy diet. A diet that is too high in protein and low in carbohydrates can lead to ketosis, a metabolic state in which the body burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
Ketosis can cause fatigue, nausea, and headaches.Individuals with specific dietary restrictions or health conditions may need to adjust their protein intake. For example, individuals with kidney disease may need to limit their protein intake to reduce the workload on their kidneys.
Individuals with gout may need to limit their intake of purine-rich foods, such as red meat and seafood, as these foods can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks.
Protein-Rich Recipes
Consuming 300 grams of protein daily requires a well-structured diet that incorporates protein-rich foods in every meal. This section provides a collection of recipes for breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks that are packed with protein. Whether you’re a seasoned cook or a beginner, these recipes offer a range of options to cater to different dietary preferences and cooking abilities.
Breakfast Recipes
- Protein Pancakes:Combine 1 cup of rolled oats, 1/2 cup of protein powder, 2 eggs, 1/2 cup of milk, and 1/4 cup of water. Blend until smooth and cook in a pan with a little oil. Top with your favorite fruit or nuts.
- Greek Yogurt Parfait:Layer 1 cup of Greek yogurt with 1/2 cup of berries, 1/4 cup of granola, and a drizzle of honey.
- Scrambled Eggs with Smoked Salmon:Scramble 2 eggs with 1/4 cup of smoked salmon, 1/4 cup of chopped bell pepper, and 1/4 cup of chopped onion.
Lunch Recipes
- Grilled Chicken Salad:Grill 4 ounces of chicken breast and slice it. Combine with 1 cup of mixed greens, 1/2 cup of cherry tomatoes, 1/2 cup of cucumber, 1/4 cup of red onion, and a drizzle of olive oil and vinegar.
- Tuna Salad Sandwich:Combine 1 can of tuna, 1/4 cup of mayonnaise, 1/4 cup of celery, 1/4 cup of red onion, and a dash of salt and pepper. Spread on whole-wheat bread.
- Lentil Soup:Simmer 1 cup of lentils in 4 cups of vegetable broth with 1/2 cup of chopped carrots, 1/2 cup of chopped celery, and 1/4 cup of chopped onion. Season with salt and pepper to taste.
Dinner Recipes
- Grilled Salmon with Roasted Vegetables:Grill 4 ounces of salmon and serve with 1 cup of roasted vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots, and potatoes.
- Chicken Stir-Fry:Stir-fry 4 ounces of chicken with 1 cup of chopped vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers. Serve over brown rice.
- Pasta with Meat Sauce:Combine 1 pound of cooked pasta with 1 cup of meat sauce made with 1 pound of ground beef, 1 cup of chopped tomatoes, and 1/2 cup of chopped onion.
Snack Recipes
- Protein Shake:Blend 1 cup of milk with 1 scoop of protein powder, 1/2 cup of fruit, and a handful of ice.
- Trail Mix:Combine 1/2 cup of nuts, 1/2 cup of seeds, and 1/4 cup of dried fruit.
- Greek Yogurt:1 cup of Greek yogurt provides around 20 grams of protein.
Tips for Enhancing Protein Content in Existing Recipes
- Add protein powder:Protein powder can be added to smoothies, soups, and baked goods to boost protein content.
- Use Greek yogurt:Greek yogurt is a high-protein substitute for regular yogurt in recipes.
- Add beans or lentils:Beans and lentils are excellent sources of plant-based protein and can be added to soups, salads, and casseroles.
- Choose lean meats:Lean meats, such as chicken, turkey, and fish, provide high-quality protein without excessive fat.
Protein Tracking and Monitoring
Monitoring protein intake is crucial for optimizing results when aiming for 300 grams daily. It ensures consistency, accountability, and allows for necessary adjustments to meet individual needs and goals.
Various methods exist for tracking protein consumption, including:
Food Diary
- Keep a written or digital record of all foods consumed, noting their protein content.
- This provides a comprehensive overview of protein intake patterns.
Mobile Apps
- Utilize apps designed to track nutrition, including protein intake.
- These apps often feature extensive food databases and user-friendly interfaces.
Online Tools
- Access online databases or calculators that provide nutritional information for various foods.
- These tools allow for quick and convenient protein tracking.
Additional Considerations
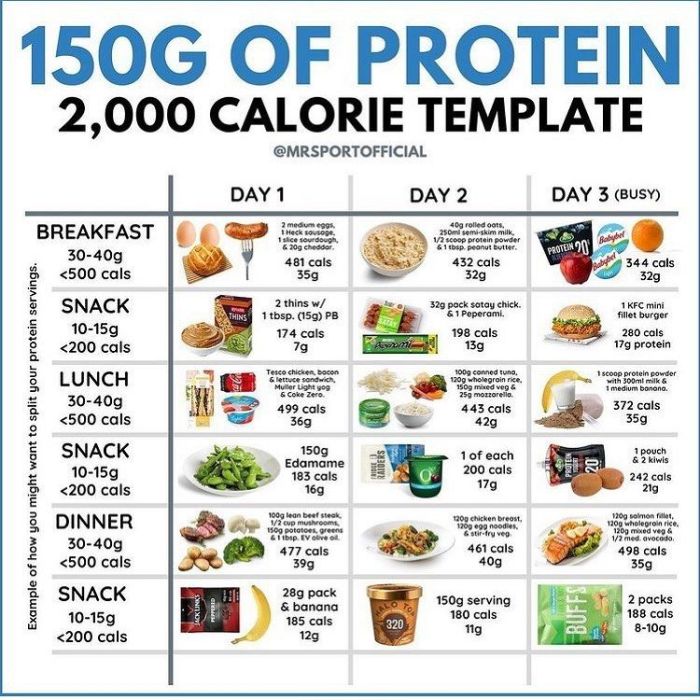
To optimize protein metabolism and reap the benefits of a high-protein diet, consider these additional factors:
Hydration
Water is crucial for numerous bodily functions, including protein metabolism. Adequate hydration ensures proper absorption and utilization of protein. Dehydration can impair protein synthesis and compromise muscle recovery.
Rest and Recovery
Sleep and rest are essential for protein synthesis. During sleep, the body releases growth hormone, which stimulates protein synthesis and muscle repair. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support optimal protein utilization.
Sustainable Protein Intake
- Variety:Include a wide range of protein sources to ensure a balanced intake of amino acids.
- Gradual Increase:Gradually increase protein intake over time to allow the body to adapt and avoid digestive issues.
- Hydration:Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support protein metabolism and prevent dehydration.
- Monitor:Track your protein intake using apps or a food journal to ensure you’re meeting your goals.
- Professional Guidance:Consult a registered dietitian or healthcare professional for personalized advice on a sustainable high-protein diet.
Wrap-Up: How Do I Get 300 Grams Of Protein A Day
In the realm of nutrition, protein reigns supreme. Embarking on a high-protein journey can transform your health and fitness goals into a reality. With careful planning, mindful eating, and a dash of creativity, achieving 300 grams of protein daily is not just a dream but a tangible goal.
Remember, consistency is key, and seeking professional guidance when necessary can ensure a safe and effective protein-rich adventure.
FAQ Resource
How can I calculate my daily protein requirements?
To determine your daily protein needs, consider factors like age, weight, activity level, and fitness goals. A general guideline is 0.8-1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight.
What are some good sources of plant-based protein?
Plant-based protein sources include lentils, beans, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and nuts. These provide essential amino acids and fiber, promoting satiety and overall well-being.
Is it safe to consume 300 grams of protein daily?
Consuming 300 grams of protein daily is generally safe for healthy individuals. However, it’s crucial to ensure adequate hydration and monitor kidney function, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions.
Can protein supplements help me reach my protein goals?
Protein supplements can be a convenient way to boost your protein intake. Whey, casein, and pea protein are popular options, each with unique benefits. Consult a healthcare professional before incorporating supplements into your routine.
How can I track my protein intake?
Tracking your protein intake can help you stay accountable and make necessary adjustments. Use food tracking apps, consult with a registered dietitian, or simply keep a food journal to monitor your protein consumption.