With tire pressure sensor location at the forefront, embark on an enlightening journey into the world of tire maintenance. Discover the intricacies of these sensors, their strategic placement, and their crucial role in ensuring your vehicle’s safety and efficiency.
Delve into the various types of tire pressure sensors, understanding their functions and applications in different vehicle models. Explore the common locations where these sensors reside, uncovering the reasons behind their specific placement.
Sensor Types and Functions
Tire pressure sensors play a vital role in monitoring and maintaining optimal tire pressure in vehicles. These sensors detect and transmit real-time data on tire pressure to the vehicle’s computer system, alerting drivers to any significant deviations. Different types of tire pressure sensors are employed in various vehicle models, each with specific functionalities:
Direct Tire Pressure Sensors
Direct tire pressure sensors are installed inside each tire and measure tire pressure directly. These sensors are typically mounted on the valve stem and consist of a pressure transducer, a transmitter, and a battery. The pressure transducer converts pressure into an electrical signal, which is then transmitted wirelessly to the vehicle’s computer system.
Direct tire pressure sensors provide highly accurate and real-time pressure readings, enabling drivers to monitor tire pressure precisely.
Indirect Tire Pressure Sensors
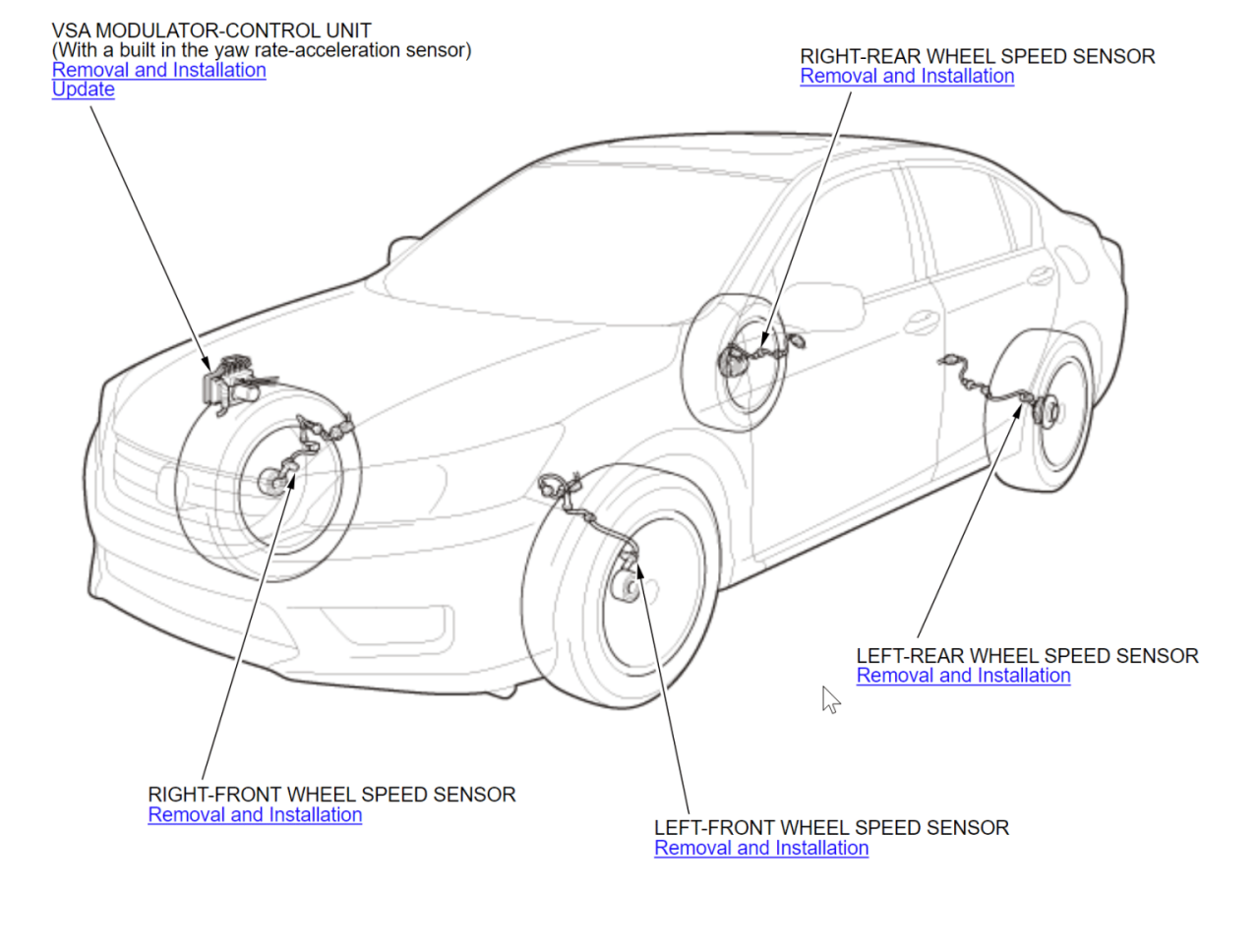
Indirect tire pressure sensors, also known as wheel speed sensors, monitor tire pressure indirectly by measuring the rotational speed of each wheel. These sensors are usually integrated into the vehicle’s anti-lock braking system (ABS) and use wheel speed variations to detect changes in tire pressure.
When tire pressure drops, the diameter of the tire decreases, causing the wheel to rotate faster. Indirect tire pressure sensors are less precise than direct sensors but are more cost-effective and require less maintenance.
Location of Sensors
Tire pressure sensors are typically installed in one of two common locations: inside the tire or on the valve stem. Each location offers specific advantages and considerations.
Inside the Tire
Sensors placed inside the tire are typically mounted on the wheel rim or the tire’s inner liner. This location provides direct access to the tire’s internal pressure, allowing for accurate readings even in dynamic driving conditions.
- Accurate readings:Direct contact with the tire’s air cavity ensures precise pressure measurements.
- Protected from external factors:Inside placement shields the sensor from road debris, weather conditions, and accidental damage.
- Requires tire disassembly:Installation and maintenance involve removing the tire from the rim, which can be time-consuming.
On the Valve Stem
Valve stem-mounted sensors are attached directly to the tire’s valve stem, where the tire is inflated. This location offers convenience and accessibility.
- Easy installation and maintenance:Sensors can be installed or replaced without removing the tire.
- Cost-effective:Valve stem sensors are generally less expensive than inside-mounted sensors.
- Exposed to external factors:Sensors may be vulnerable to road debris, weather conditions, and accidental damage.
Installation and Replacement Procedures
Installing and replacing tire pressure sensors is a relatively straightforward process, but it’s important to follow the correct steps to ensure accuracy and safety.
Before you begin, gather the necessary tools and materials, including a tire pressure gauge, a torque wrench, a jack and jack stands, and new tire pressure sensors.
Safety Precautions, Tire pressure sensor location
- Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake.
- Allow the tires to cool before working on them.
- Wear gloves and safety glasses when handling tire pressure sensors.
Installation
- Remove the old tire pressure sensor by unscrewing it from the valve stem.
- Apply a small amount of sealant to the threads of the new sensor.
- Screw the new sensor onto the valve stem and tighten it to the specified torque using a torque wrench.
- Reset the tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Replacement
- Follow the steps for installation, but replace the old sensor with the new one.
- If the sensor is damaged or malfunctioning, it may need to be replaced by a qualified technician.
System Monitoring and Troubleshooting
The vehicle’s computer system constantly monitors tire pressure sensors using wireless signals. Each sensor transmits its pressure readings to the computer, which then calculates the overall tire pressure. If any sensor detects a significant change in pressure, it sends an alert to the computer.
Warning Indicators and Alerts
When there are issues with tire pressure sensors, the vehicle’s computer system may trigger several warning indicators and alerts:
-
-*Low Tire Pressure Warning Light
This light illuminates when one or more tires are significantly underinflated.
-*Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) Malfunction Indicator
This light indicates a problem with the TPMS itself, such as a sensor failure or communication issue.
-*Audible Warning
Some vehicles may emit an audible warning chime when a tire pressure issue is detected.
-*Dashboard Display
The vehicle’s dashboard may display a message or code indicating the specific tire or sensor affected.
Benefits of Tire Pressure Sensors

Tire pressure sensors provide a myriad of advantages for vehicle owners, enhancing safety, fuel efficiency, and extending tire lifespan.
Studies conducted by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) reveal that underinflated tires are a significant factor in tire-related accidents, accounting for approximately 330 fatalities and 10,000 injuries annually in the United States. Tire pressure sensors mitigate this risk by alerting drivers to any deviations from optimal tire pressure, allowing them to promptly address the issue and prevent potential hazards.
Fuel Efficiency
Maintaining proper tire pressure is crucial for optimal fuel efficiency. Underinflated tires increase rolling resistance, which in turn demands more energy from the engine to maintain speed. This increased energy consumption translates into reduced fuel efficiency. Tire pressure sensors monitor tire pressure in real-time, ensuring that it remains within the recommended range and minimizing rolling resistance.
As a result, vehicles equipped with tire pressure sensors can achieve better fuel mileage, reducing fuel consumption and lowering operating costs.
Tire Lifespan
Proper tire pressure also plays a vital role in extending tire lifespan. Underinflated tires experience uneven wear, leading to premature tread loss and reduced tire life. Tire pressure sensors continuously monitor tire pressure, alerting drivers to any deviations that could compromise tire integrity.
By maintaining optimal tire pressure, drivers can maximize tire lifespan, reducing the frequency of tire replacements and saving money in the long run.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance and calibration of tire pressure sensors are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and extending their lifespan. Proper maintenance helps detect and address potential issues, while calibration ensures accurate readings and reliable alerts.
Recommended Intervals
- Inspect tire pressure sensors visually every 6-12 months.
- Calibrate tire pressure sensors every 2-3 years or as recommended by the manufacturer.
Maintenance Procedures
- Check for any physical damage, corrosion, or loose connections.
- Clean the sensors and valve stems using a soft brush or cloth.
- Tighten any loose components, such as valve caps or sensor mounts.
- Replace damaged or faulty sensors as needed.
Calibration Procedures
- Use a dedicated tire pressure sensor calibration tool.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration.
- Verify the accuracy of the sensors by comparing the readings with a reliable tire pressure gauge.
Final Conclusion: Tire Pressure Sensor Location
In conclusion, tire pressure sensor location plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal tire performance and overall vehicle safety. By understanding their types, functions, and placement, you empower yourself to proactively care for your tires, ensuring a smooth and worry-free driving experience.
User Queries
What are the different types of tire pressure sensors?
There are two main types: direct and indirect tire pressure sensors. Direct sensors measure the pressure inside the tire directly, while indirect sensors estimate pressure based on wheel speed and rotation.
Why are tire pressure sensors typically installed near the valve stem?
This location provides easy access for maintenance and replacement, as well as optimal signal transmission to the vehicle’s computer system.
How often should tire pressure sensors be calibrated?
Regular calibration is recommended every 2-3 years or whenever tires are replaced to ensure accurate readings and optimal performance.