The mass air flow sensor location is a crucial aspect of vehicle maintenance and performance. This comprehensive guide will delve into the location, function, and significance of the MAF sensor, providing valuable insights for car owners and enthusiasts alike.
The MAF sensor plays a vital role in regulating the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Understanding its location and how to maintain it is essential for keeping your vehicle running smoothly.
Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF)
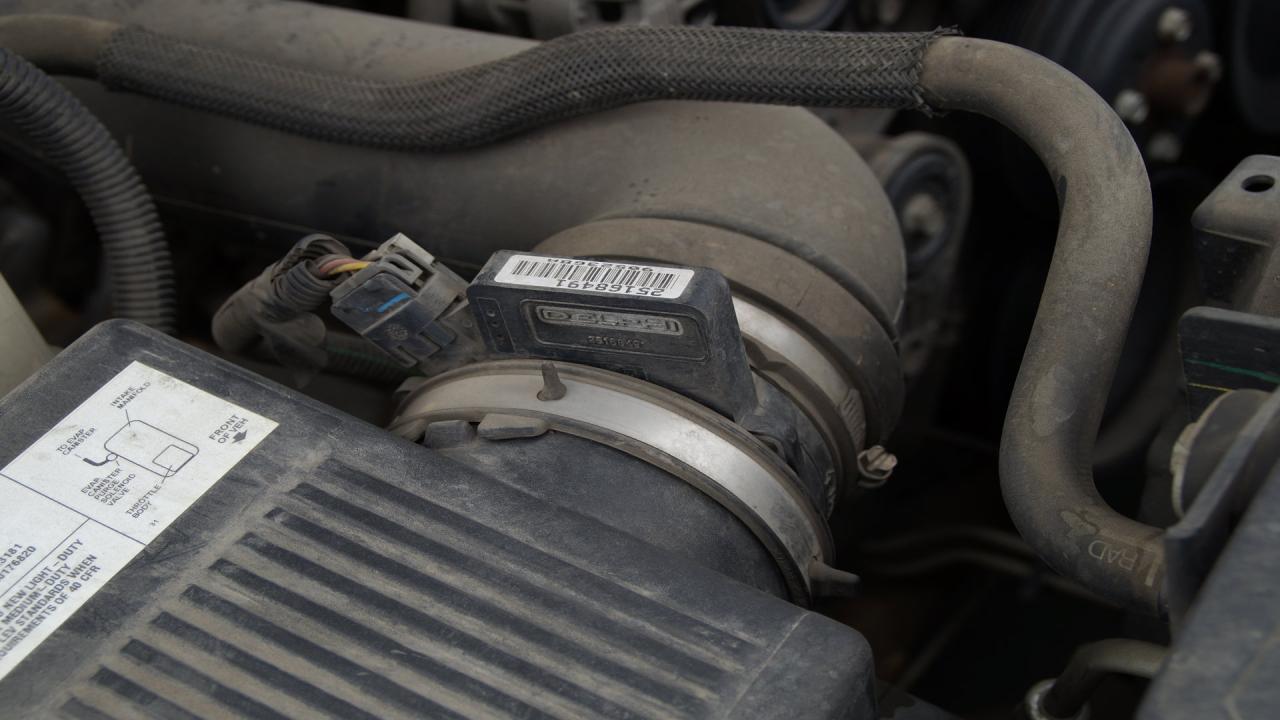

A mass air flow (MAF) sensor is a crucial component in a vehicle’s engine management system, responsible for measuring the mass of air entering the engine. This information is vital for the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the optimal air-fuel ratio for efficient combustion.
Typical Location of MAF Sensors
MAF sensors are typically located in the air intake system, positioned between the air filter and the throttle body. This placement allows them to accurately measure the airflow before it enters the engine’s cylinders.
The specific location of the MAF sensor may vary depending on the vehicle make and model. In most modern vehicles, the MAF sensor is housed in a dedicated housing or tube within the air intake system.
MAF Sensor Replacement
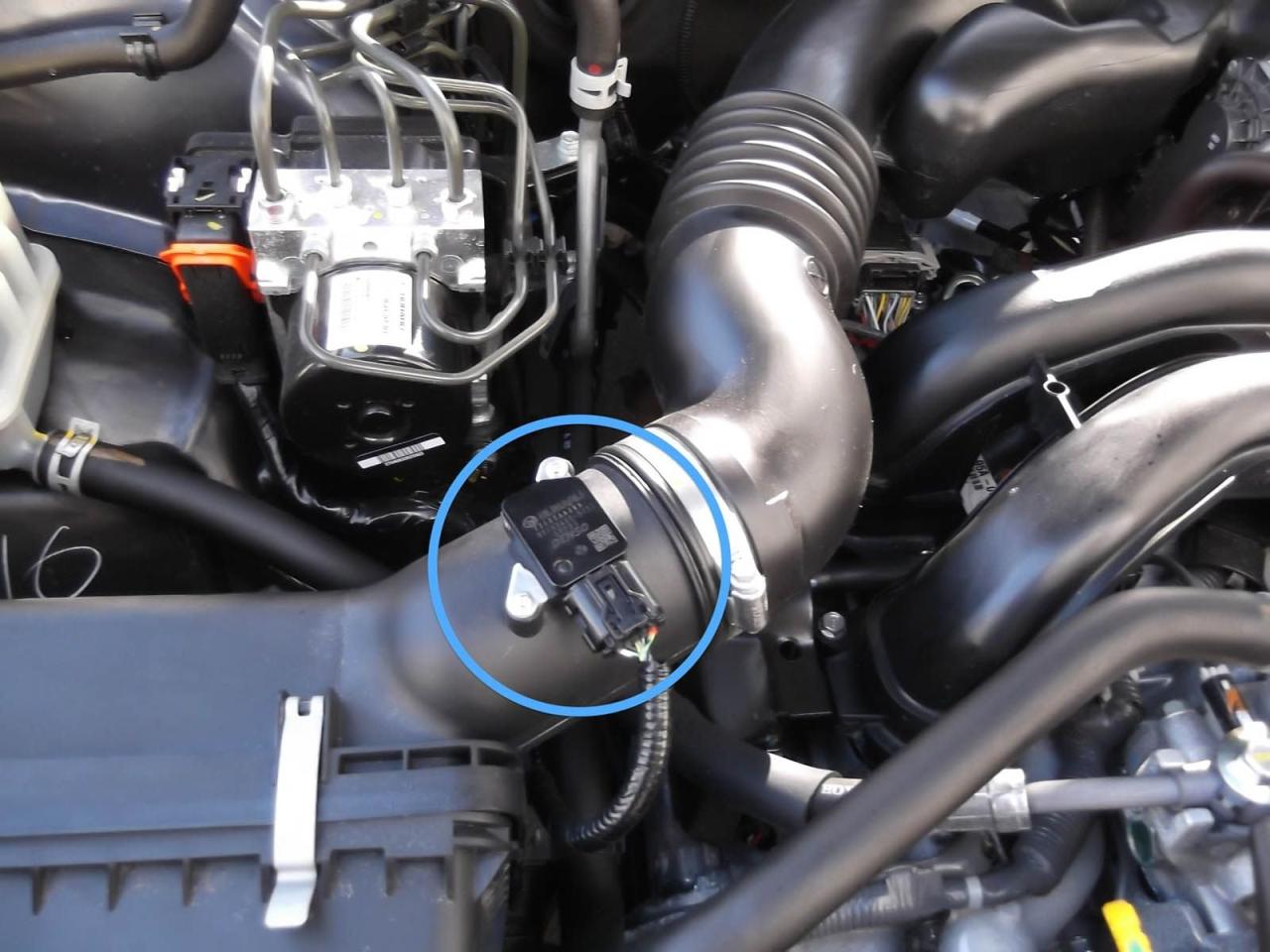

A faulty Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor can lead to a range of issues in your vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a faulty MAF sensor is crucial to ensure timely replacement.
Common signs include rough idling, hesitation or stalling during acceleration, reduced fuel economy, black smoke from the exhaust, and illuminated Check Engine Light.
Steps Involved in Replacing a MAF Sensor
Replacing a MAF sensor typically involves the following steps:
- Safety Precautions:Disconnect the negative terminal of the battery to prevent electrical shocks.
- Locate the MAF Sensor:The MAF sensor is usually located in the air intake system, between the air filter and the throttle body.
- Disconnect Electrical Connector:Unplug the electrical connector from the MAF sensor.
- Remove Mounting Bolts:Unscrew the mounting bolts holding the MAF sensor in place.
- Replace MAF Sensor:Remove the old MAF sensor and replace it with a new one.
- Tighten Mounting Bolts:Tighten the mounting bolts to secure the new MAF sensor.
- Reconnect Electrical Connector:Plug the electrical connector back into the MAF sensor.
- Reconnect Battery:Reconnect the negative terminal of the battery.
Locating the MAF Sensor in Various Vehicle Models
The location of the MAF sensor may vary depending on the vehicle model. Here are some common locations:
- Front of Air Filter Housing:Some vehicles have the MAF sensor mounted directly on the front of the air filter housing.
- Inside Air Intake Tube:In other vehicles, the MAF sensor is located inside the air intake tube, just before the throttle body.
- Behind Throttle Body:In some cases, the MAF sensor is placed behind the throttle body.
Refer to your vehicle’s service manual or consult a qualified mechanic if you have difficulty locating the MAF sensor.
MAF Sensor Maintenance
Regular maintenance of the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Neglecting its upkeep can lead to various issues that may affect the vehicle’s drivability and overall health.
Cleaning Procedures
Cleaning the MAF sensor is a straightforward process that should be performed periodically, especially in dusty or polluted environments. The recommended cleaning method involves using a specialized MAF sensor cleaner spray, which can be purchased at most auto parts stores.
- Locate the MAF sensor, which is typically situated in the air intake system between the air filter and the throttle body.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Spray the cleaner onto the sensor element, avoiding contact with the wires or other electrical components.
- Allow the cleaner to sit for a few minutes to dissolve any accumulated dirt or debris.
- Use a clean cloth or compressed air to gently remove any remaining residue.
- Reconnect the electrical connector and start the engine to allow the sensor to recalibrate.
Troubleshooting MAF Sensor Issues: Mass Air Flow Sensor Location
Identifying and resolving issues with your MAF sensor is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance. Common causes of MAF sensor malfunctions include:
- Contamination due to dirt, debris, or oil buildup
- Damaged or loose wiring connections
- Faulty sensor element
- Vacuum leaks
Diagnostic Flowchart for Troubleshooting MAF Sensor Problems
Follow this step-by-step flowchart to diagnose MAF sensor problems:
- Check for contamination:Inspect the sensor for dirt, debris, or oil buildup. Clean it with MAF sensor cleaner if necessary.
- Examine wiring:Check for loose or damaged wiring connections. Ensure the sensor is securely plugged in.
- Test MAF sensor functionality:Use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s output voltage or resistance. Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Inspect vacuum lines:Check for leaks or cracks in the vacuum lines connected to the MAF sensor.
Using a Multimeter to Test MAF Sensor Functionality
To test MAF sensor functionality using a multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to measure voltage or resistance, depending on the sensor type.
- Connect the positive lead of the multimeter to the sensor’s signal wire.
- Connect the negative lead to the sensor’s ground wire.
- Start the engine and let it idle. Record the sensor’s output voltage or resistance.
- Compare the readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. If the readings are significantly different, the sensor may be faulty.
MAF Sensor Design and Technology
MAF sensors have evolved significantly over the years, with various types and technologies emerging to meet the evolving demands of engine management systems. These sensors play a crucial role in determining the mass of air entering the engine, which is essential for precise fuel injection and optimal engine performance.
Types of MAF Sensors
- Hot-wire MAF sensors:Utilize a heated wire that cools when airflow passes over it. The amount of cooling is proportional to the mass airflow rate.
- Hot-film MAF sensors:Similar to hot-wire sensors, but use a thin film instead of a wire, offering faster response times and improved accuracy.
- Karman vortex MAF sensors:Employ a bluff body placed in the airflow path, creating vortices whose frequency is proportional to the mass airflow rate.
- Speed density MAF sensors:Calculate mass airflow rate indirectly using manifold absolute pressure and temperature sensors, along with engine speed.
- Laser Doppler velocimetry MAF sensors:Utilize lasers to measure the velocity of air particles, providing highly accurate and real-time mass airflow data.
Principles of Operation, Mass air flow sensor location
Hot-wire and hot-film sensors operate on the principle of convective heat transfer. As air flows over the heated element, it removes heat, causing a change in its resistance. This resistance change is measured and converted into a mass airflow rate signal.
Karman vortex sensors create a series of vortices behind the bluff body. The frequency of these vortices is directly proportional to the mass airflow rate. The sensor detects these vortices using pressure or temperature sensors.
Speed density sensors rely on the relationship between manifold pressure, temperature, and engine speed to estimate mass airflow rate. This method is less accurate than direct measurement but is often used in older vehicles.
Laser Doppler velocimetry sensors use the Doppler effect to measure the velocity of air particles. By knowing the velocity and cross-sectional area of the airflow path, the mass airflow rate can be calculated.
Advancements in MAF Sensor Technology
Recent advancements in MAF sensor technology include:
- Increased accuracy and sensitivity:Modern MAF sensors provide highly precise and reliable mass airflow measurements.
- Faster response times:Advanced sensors can respond to changes in airflow more quickly, improving engine responsiveness and performance.
- Improved durability:New materials and designs enhance the longevity and reliability of MAF sensors, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Integration with other sensors:MAF sensors are increasingly integrated with other sensors, such as temperature and pressure sensors, to provide comprehensive engine management data.
MAF Sensor Data Interpretation

The MAF sensor data is a crucial input for the engine control unit (ECU) to determine the air mass entering the engine. The ECU uses this information to calculate the appropriate fuel injection quantity and ignition timing for optimal engine performance and efficiency.
From the MAF sensor data, the ECU can derive several parameters, including:
- Air mass flow rate (g/s): The mass of air flowing through the intake manifold per unit time.
- Air-fuel ratio: The ratio of air mass to fuel mass in the combustion mixture.
- Engine load: The percentage of the engine’s maximum power output that is being used.
These parameters are used by the ECU for various engine control functions, such as:
- Fuel injection: The ECU adjusts the fuel injection quantity based on the air mass flow rate to maintain the desired air-fuel ratio.
- Ignition timing: The ECU advances or retards the ignition timing based on the engine load to optimize combustion efficiency.
- EGR control: The ECU uses the air mass flow rate to determine the appropriate amount of exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) to reduce NOx emissions.
Additionally, MAF sensor data can be used for engine diagnostics. By analyzing the sensor signal, technicians can identify potential issues with the air intake system, such as:
- Vacuum leaks: A sudden drop in MAF sensor signal may indicate a vacuum leak in the intake system.
- Clogged air filter: A gradual decrease in MAF sensor signal over time may indicate a clogged air filter.
- Faulty MAF sensor: An erratic or inconsistent MAF sensor signal may indicate a faulty sensor.
MAF Sensor and Fuel Economy
The MAF sensor plays a crucial role in determining the amount of fuel injected into the engine. It measures the mass of air entering the engine, which is a key factor in calculating the optimal air-fuel ratio. A faulty MAF sensor can lead to inaccurate fuel delivery, resulting in reduced fuel economy.
Tips to Optimize MAF Sensor Performance
- Regular Cleaning:Regularly clean the MAF sensor to remove dirt and debris that can obstruct airflow measurement.
- Proper Installation:Ensure the MAF sensor is securely installed and the electrical connections are tight.
- Avoid Over-Oiling:Avoid over-oiling the air filter, as excess oil can contaminate the MAF sensor.
- Use High-Quality Filters:Use high-quality air filters to prevent dust and debris from entering the engine and reaching the MAF sensor.
- Check for Leaks:Inspect the intake system for any leaks that can introduce unmetered air, affecting MAF sensor readings.
Summary
In conclusion, the mass air flow sensor location is a key factor in ensuring proper engine operation. By understanding its location, you can effectively troubleshoot issues, perform maintenance, and optimize fuel efficiency. Regular monitoring and care of the MAF sensor will contribute to the longevity and performance of your vehicle.
FAQ Explained
Where is the MAF sensor typically located?
The MAF sensor is usually situated in the air intake system, between the air filter and the throttle body.
What are the signs of a faulty MAF sensor?
Symptoms of a faulty MAF sensor include rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and decreased fuel economy.
How often should I clean the MAF sensor?
Regular cleaning of the MAF sensor is recommended every 12,000 to 15,000 miles or as per the manufacturer’s guidelines.