ABS sensor location plays a pivotal role in ensuring the optimal performance of a vehicle’s braking system. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the purpose, types, installation, maintenance, diagnostics, and replacement of ABS sensors, providing you with a thorough understanding of their crucial function.
ABS sensors, strategically positioned at specific locations on a vehicle, serve as the eyes and ears of the anti-lock braking system. They monitor wheel speed and transmit data to the ABS control module, enabling it to modulate brake pressure and prevent wheel lock-up during braking, enhancing vehicle stability and safety.
ABS Sensor Location and Function

ABS (Anti-lock Braking System) sensors play a crucial role in modern vehicles’ braking systems. These sensors monitor wheel speed and detect when a wheel is about to lock up during braking, allowing the ABS system to modulate brake pressure and prevent the wheel from skidding.
ABS sensors are typically located at each wheel hub, mounted on the wheel bearing or knuckle. The sensor uses a magnetic or optical sensor to measure the speed of the wheel. When the wheel speed drops suddenly, indicating that the wheel is about to lock up, the ABS sensor sends a signal to the ABS control unit, which then reduces the brake pressure to that wheel.
ABS Sensor Locations
ABS sensors are typically located in the following areas:
- Front wheel hubs
- Rear wheel hubs
- Differential (for vehicles with all-wheel drive)
- Driveshaft (for vehicles with rear-wheel drive)
ABS Sensor Types and Designs
ABS sensors are available in various types, each with its unique design and operating principles. Understanding the different types of ABS sensors is essential for selecting the appropriate sensor for specific applications.
Active ABS Sensors
Active ABS sensors generate their own magnetic field using an internal coil. When a ferrous metal object, such as a wheel hub, passes through the magnetic field, it induces an electrical signal in the sensor. The frequency and amplitude of the electrical signal are proportional to the speed of the wheel.
Passive ABS Sensors
Passive ABS sensors rely on a permanent magnet to generate a magnetic field. As a ferrous metal object passes through the magnetic field, it causes a change in the magnetic field strength. This change in magnetic field strength is detected by the sensor and converted into an electrical signal.
Hall-Effect ABS Sensors
Hall-effect ABS sensors utilize the Hall effect to detect the presence of a magnetic field. When a magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the sensor, it creates a voltage difference across the sensor’s terminals. The magnitude of the voltage difference is proportional to the strength of the magnetic field.
In ABS sensors, the magnetic field is generated by a ferrous metal object passing through the sensor’s magnetic field.
ABS Sensor Installation and Maintenance
Installing and maintaining ABS sensors is crucial for optimal braking performance. Follow these steps for proper installation:1.
-
-*Locate the ABS sensor mounting points
Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or consult a mechanic.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
-*Clean the mounting surface
Remove any dirt, rust, or debris to ensure a secure fit.
-*Apply a thin layer of thread sealant
This helps prevent leaks and corrosion.
-*Tighten the ABS sensor to the specified torque
Use a torque wrench to avoid over-tightening or under-tightening.
-*Connect the electrical connector
Ensure a secure connection and protect it from moisture.
Regular maintenance is essential for reliable ABS operation. Inspect the sensors and wiring for any damage or corrosion. Clean the sensors with a brake cleaner and inspect the wiring for breaks or shorts. If any issues are found, replace the affected components promptly.
Common Troubleshooting Procedures
If the ABS system is not functioning properly, troubleshooting is necessary. Common issues include:
-
-*Faulty sensor
Replace the faulty sensor.
-*Damaged wiring
Repair or replace the damaged wiring.
-*Low brake fluid
Check and refill the brake fluid reservoir.
-*Air in the ABS system
Bleed the ABS system to remove any trapped air.
-*Faulty ABS module
Diagnose and repair or replace the ABS module if necessary.
Regular maintenance and proper troubleshooting ensure optimal ABS performance, enhancing vehicle safety and braking efficiency.
ABS Sensor Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
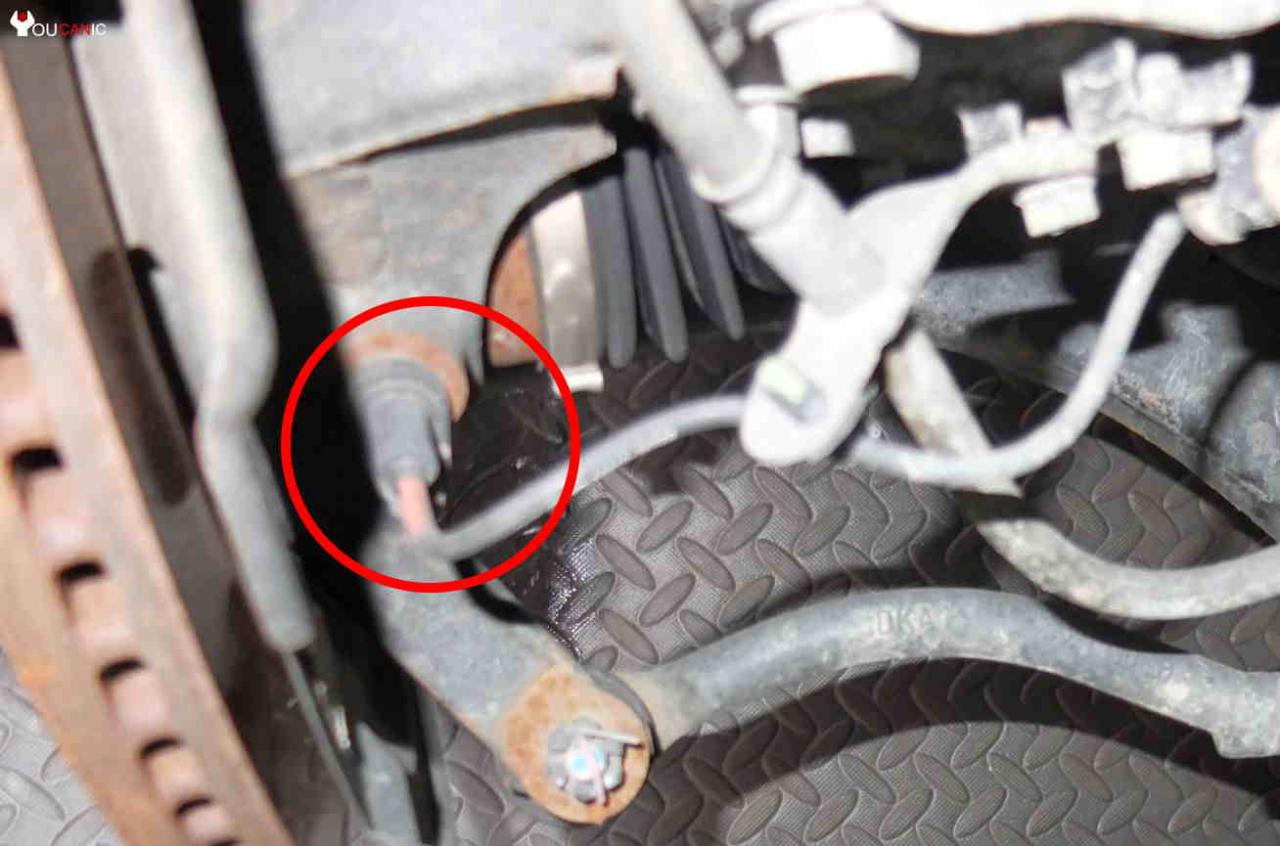

ABS sensors play a crucial role in ensuring optimal braking performance and vehicle safety. When these sensors malfunction, they can lead to reduced braking efficiency and potentially dangerous situations. Therefore, it is essential to be able to diagnose and troubleshoot faulty ABS sensors effectively.
Symptoms of Faulty ABS Sensors
Several symptoms can indicate a faulty ABS sensor:
- Illuminated ABS warning light on the dashboard
- Erratic or inconsistent braking
- ABS system not engaging during braking
- Reduced braking performance on slippery surfaces
- Vehicle pulling to one side during braking
Diagnostic Codes, Abs sensor location
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) can provide valuable information about the nature of the ABS sensor fault. Common DTCs associated with ABS sensors include:
- C0031 – Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction
- C0032 – Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction
- C0033 – Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction
- C0034 – Left Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Malfunction
- C0035 – ABS Sensor Power Supply Circuit Malfunction
Diagnostic Procedures
To diagnose a faulty ABS sensor, several procedures can be followed:
- Visual Inspection:Inspect the ABS sensor for any visible damage, such as cuts, cracks, or corrosion on the wiring.
- Multimeter Testing:Using a multimeter, measure the resistance of the ABS sensor. A faulty sensor will typically have an open circuit (infinite resistance) or a short circuit (zero resistance).
- Signal Measurement:Connect an oscilloscope to the ABS sensor output and observe the signal waveform. A faulty sensor may produce an abnormal or distorted waveform.
- Scan Tool Diagnostics:Advanced scan tools can access the ABS module and retrieve specific DTCs related to the ABS sensor fault.
By following these diagnostic procedures, technicians can effectively identify and troubleshoot faulty ABS sensors, ensuring the proper functioning of the ABS system and maintaining optimal vehicle safety.
ABS Sensor Replacement and Calibration: Abs Sensor Location

Replacing an ABS sensor is a critical task that requires precision and attention to detail. The process may vary slightly depending on the vehicle model, but generally involves the following steps:
1. Safety first
Ensure the vehicle is parked on a level surface, the parking brake is engaged, and the wheels are chocked to prevent movement.
2. Locate the ABS sensor
Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or online resources to identify the location of the ABS sensor that needs replacement.
3. Disconnect the electrical connector
Locate the electrical connector attached to the ABS sensor and carefully disconnect it.
4. Remove the mounting bolts
Using appropriate tools, remove the mounting bolts or screws that hold the ABS sensor in place.
5. Extract the old sensor
Gently pull the old ABS sensor out of its housing. Be cautious not to damage the sensor or its wiring harness.
6. Install the new sensor
Insert the new ABS sensor into the housing and secure it with the mounting bolts or screws.
7. Reconnect the electrical connector
Reattach the electrical connector to the new ABS sensor.
8. Reset the ABS system
In some cases, the ABS system may need to be reset after replacing a sensor. Refer to the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions on resetting the ABS system.Once the ABS sensor is replaced, it is crucial to perform calibration to ensure accurate readings and optimal performance.
Calibration involves using a scan tool or diagnostic equipment to adjust the sensor’s output signal to match the vehicle’s specific parameters. This process ensures that the ABS system receives accurate wheel speed data and can effectively modulate brake pressure during braking.
Importance of ABS Sensor Calibration
ABS sensor calibration is essential for the following reasons:
Accurate wheel speed readings
Calibration ensures that the ABS sensor provides precise wheel speed data to the ABS control module.
Optimal ABS performance
Proper calibration optimizes the ABS system’s ability to prevent wheel lock-up during braking, ensuring maximum stopping power and stability.
Reduced false triggering
Calibration minimizes the chances of false ABS activation due to incorrect sensor readings.
Enhanced safety
Accurate ABS sensor calibration contributes to overall vehicle safety by improving braking performance and reducing the risk of accidents.
Final Thoughts
In summary, ABS sensors are essential components of a vehicle’s braking system, ensuring safe and controlled braking. Understanding their location, types, and maintenance procedures empowers vehicle owners and technicians to maintain optimal ABS performance, contributing to overall vehicle safety.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the common locations of ABS sensors?
ABS sensors are typically mounted on the wheel hubs, knuckles, or suspension components near the wheels.
How do I identify a faulty ABS sensor?
Symptoms of a faulty ABS sensor include illuminated ABS warning light, reduced braking performance, and ABS activation during normal braking.
Can I replace an ABS sensor myself?
While it is possible to replace an ABS sensor yourself, it is recommended to consult a qualified mechanic for proper installation and calibration.