Is shift solenoid a and b the same – Are shift solenoids A and B the same? This question arises when discussing the intricate inner workings of a transmission system. In this article, we delve into the similarities and differences between shift solenoids A and B, exploring their design, functionality, and troubleshooting techniques.
Read on to unravel the mysteries surrounding these crucial components.
Shift solenoids play a vital role in ensuring smooth and efficient gear shifting. Understanding their characteristics and maintenance requirements is essential for prolonging transmission life and preventing costly repairs.
Introduction
Shift solenoids are essential components in a vehicle’s transmission system, responsible for regulating the flow of transmission fluid to engage and disengage gears. They are typically positioned within the transmission’s valve body and operate in conjunction with the transmission control module (TCM) to execute smooth and efficient gear shifts.
Modern transmissions often employ multiple shift solenoids, designated as A and B, to provide greater control and precision during gear changes. These solenoids work in tandem to modulate the flow of fluid through the transmission’s hydraulic circuits, enabling the transmission to select the appropriate gear based on driving conditions.
Similarities and Differences between Shift Solenoid A and B
Shift solenoids A and B play crucial roles in the functioning of an automatic transmission system. While they share certain similarities in design and operation, they also exhibit some key differences. Understanding these similarities and differences is essential for proper diagnosis and repair of transmission issues.
If you’re a fan of classic cars, then you’ll definitely want to check out the 1970 Plymouth Barracuda. This iconic muscle car is known for its sleek design and powerful engine. It’s a true classic that’s sure to turn heads wherever it goes.
To learn more about the 1970 Plymouth Barracuda, including its specs and history, head over to: Plymouth Barracuda 1970
Shared Features and Functionalities
Both shift solenoids A and B are electromechanical devices that control the flow of transmission fluid within the transmission. They are designed to regulate the engagement and disengagement of specific gear sets, enabling smooth gear shifting.
The solenoids consist of a coil, a plunger, and a valve. When an electrical current passes through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that moves the plunger. The movement of the plunger opens or closes the valve, allowing transmission fluid to flow through specific channels and engage or disengage the corresponding gear set.
Differences in Operation and Characteristics, Is shift solenoid a and b the same
Despite their shared features, shift solenoid A and B differ in their specific operation and characteristics:
- Control:Shift solenoid A is typically responsible for controlling the engagement and disengagement of lower gears (e.g., 1st, 2nd, and 3rd gears), while shift solenoid B controls higher gears (e.g., 4th and 5th gears).
- Timing:The timing of the activation and deactivation of shift solenoids A and B is critical for smooth gear shifting. Solenoid A is usually activated before solenoid B to ensure proper engagement of lower gears, while solenoid B is activated later to engage higher gears.
- Pressure:Shift solenoid A typically operates at a higher pressure than shift solenoid B. This higher pressure is necessary to overcome the increased resistance encountered when engaging lower gears.
Troubleshooting Shift Solenoid A and B
Troubleshooting shift solenoids A and B involves identifying common symptoms of failure, diagnosing and testing the solenoids, and understanding replacement procedures and precautions. By following these steps, you can effectively resolve issues related to shift solenoid A and B, ensuring smooth and reliable transmission operation.
Common symptoms of shift solenoid failure include:
- Delayed or erratic gear shifts
- Harsh or slipping gears
- Transmission warning lights or error codes
- Reduced fuel efficiency
To diagnose and test shift solenoid A and B, you can use a scan tool to read transmission fault codes. These codes can indicate which solenoid is malfunctioning. You can also perform a resistance test on the solenoids using a multimeter to check for continuity and proper electrical function.
Replacement Procedures and Precautions
Replacing shift solenoid A or B requires specific procedures and precautions. Here are the general steps:
- Gather necessary tools and replacement solenoids.
- Disconnect the battery to prevent electrical accidents.
- Locate and remove the transmission pan.
- Identify and remove the faulty solenoid.
- Install the new solenoid and tighten it to the specified torque.
- Reinstall the transmission pan and reconnect the battery.
- Use only OEM or high-quality replacement solenoids.
- Ensure proper alignment and torque when installing the solenoids.
- Inspect the transmission fluid for contamination or debris.
- Reset the transmission control module (TCM) after replacement.
- Precise shift timing: Electronic controls ensure precise shift timing, reducing driveline shock and improving overall driving experience.
- Adaptive shift strategies: Sensors provide real-time feedback, allowing the transmission to adapt its shift patterns based on driving conditions, such as load, road grade, and driver input.
- Improved fuel efficiency: Optimized shift points minimize engine speed, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Intelligent shift control: Advanced algorithms will enable shift solenoids to make autonomous decisions based on a wider range of inputs.
- Integrated sensors: Solenoids may incorporate sensors to monitor transmission parameters, providing real-time data for diagnostics and optimization.
- Electrically actuated solenoids: Solenoids operated by electric motors offer faster response times and greater precision.
Precautions to consider during replacement include:
Maintenance and Care of Shift Solenoids: Is Shift Solenoid A And B The Same
Shift solenoids play a crucial role in the smooth and efficient operation of automatic transmissions. To ensure optimal performance and longevity, proper maintenance and care are essential. Here are some key recommendations:
Regular Fluid Changes and Transmission Servicing
Regular fluid changes are paramount for maintaining the health of shift solenoids. Transmission fluid lubricates and cools the solenoids, preventing wear and tear. It also helps remove contaminants that can interfere with solenoid operation. Transmission servicing involves replacing the fluid filter and inspecting the transmission for any potential issues.
If you’re considering turning off your vehicle’s Vehicle Dynamics Control (VDC) system, you may want to reconsider. While it might seem like a good idea to have more control over your car, especially if you’re a skilled driver, VDC is actually there to help you stay safe.
It can help prevent you from losing control of your car in slippery conditions or when you’re cornering too quickly. For more information on the importance of VDC, check out this article: Is It Safe to Drive with VDC Off?
This comprehensive service helps keep the transmission and shift solenoids in top condition.
Preventing Premature Failure
Several factors can contribute to premature failure of shift solenoids. One common cause is overheating due to insufficient fluid levels or clogged transmission filters. Another is electrical faults, such as shorts or open circuits. To prevent these issues, ensure the transmission fluid is at the proper level and that the transmission filter is replaced regularly.
Additionally, avoid excessive towing or hauling, as this can put extra strain on the transmission and solenoids.
Advanced Considerations
In advanced transmission systems, shift solenoids play a crucial role in optimizing gear shifting, enhancing performance, and improving fuel efficiency.
Electronic controls and sensors have revolutionized shift solenoid operation. These systems monitor engine speed, vehicle speed, throttle position, and other parameters to determine the optimal shift points and actuate the solenoids accordingly.
Impact of Electronic Controls and Sensors
Future Developments and Trends
As transmission technology continues to evolve, shift solenoids will play an increasingly important role:
Closure
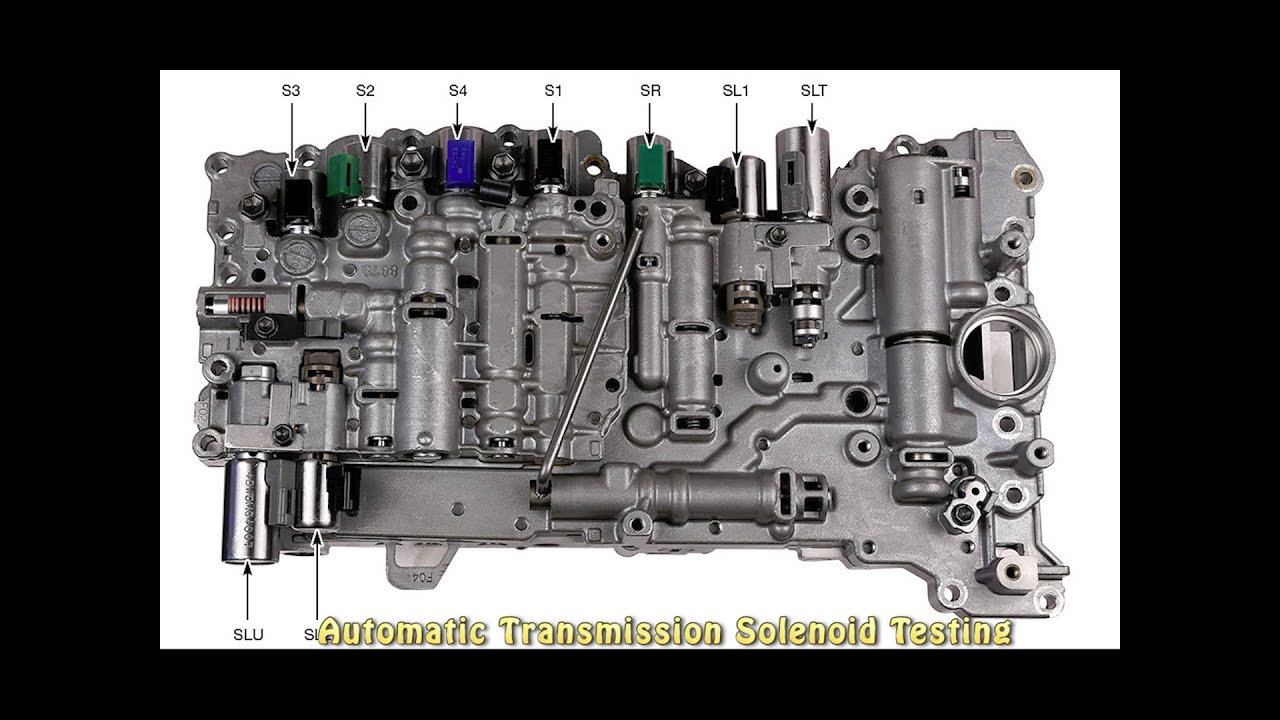
In conclusion, while shift solenoids A and B share similarities in design and function, they may exhibit subtle differences depending on the specific transmission system. Accurate diagnosis and replacement are crucial for optimal transmission performance. Regular maintenance and fluid changes can extend the lifespan of these solenoids, ensuring a smooth and trouble-free driving experience.
Questions Often Asked
Are shift solenoids A and B interchangeable?
Not necessarily. While they may share similarities, it’s essential to refer to the specific transmission system’s documentation for compatibility.
What are the common symptoms of shift solenoid failure?
Delayed or harsh gear shifting, slipping gears, and illuminated check engine light are potential indicators.
How can I test shift solenoids A and B?
Using a multimeter to measure resistance and continuity can help identify faulty solenoids.