Throttle position sensor location plays a pivotal role in understanding the intricate workings of a vehicle’s engine. This comprehensive guide delves into the purpose, location, and troubleshooting techniques associated with this crucial sensor, providing a thorough exploration for both enthusiasts and professionals alike.
The content of the second paragraph provides descriptive and clear information about the topic.
Throttle Position Sensor Location Overview
A throttle position sensor (TPS) is a critical component in a vehicle’s engine management system. It monitors the position of the throttle valve, which controls the amount of air entering the engine. This information is used by the engine control unit (ECU) to calculate the appropriate fuel injection and ignition timing.
The TPS is typically located on the throttle body, which is mounted on the intake manifold. It consists of a variable resistor that changes resistance as the throttle valve moves. This change in resistance is detected by the ECU, which then adjusts the engine’s performance accordingly.
Types of TPS Designs
There are two main types of TPS designs:
- Contact TPS:These sensors use a physical contact between a wiper and a resistive element. As the throttle valve moves, the wiper slides along the resistive element, changing the resistance.
- Non-contact TPS:These sensors use a non-contact method, such as a magnetic or optical sensor, to detect the position of the throttle valve. This type of sensor is more durable and reliable than contact TPS.
Identifying Throttle Position Sensor Location
Locating the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) accurately is crucial for proper engine performance and fuel efficiency. Here are some methods to identify the TPS location on different engine types:
On Carbureted Engines
The TPS is typically mounted on the carburetor’s throttle shaft or linkage. It may have a single or multiple connectors with colored wires.
On Fuel-Injected Engines
The TPS is usually located on the throttle body or intake manifold. It is often connected to the throttle linkage or throttle shaft and has a multi-pin connector.
Tips for Finding the TPS
- Consult the vehicle’s service manual for specific instructions.
- Look for a sensor with a connector and wires near the throttle body or carburetor.
- Follow the throttle linkage or cable to locate the sensor attached to it.
- Check for a sensor with a lever or arm that moves with the throttle.
TPS Replacement Procedures
Replacing a Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is a relatively straightforward procedure that can be completed in under an hour with the right tools and safety precautions. Before starting, ensure you have the correct replacement TPS for your vehicle and gather the necessary tools, including a socket wrench set, screwdrivers, and a multimeter.
Safety is paramount when working on any vehicle. Disconnect the battery’s negative terminal to prevent electrical shocks. Allow the engine to cool completely before starting any work to avoid burns.
Removing the Old TPS
- Locate the TPS on the throttle body. It is usually secured by two or three bolts.
- Disconnect the electrical connector from the TPS.
- Use a socket wrench to remove the bolts holding the TPS in place.
- Carefully remove the old TPS from the throttle body.
Installing the New TPS
- Place the new TPS onto the throttle body and secure it with the bolts.
- Reconnect the electrical connector to the TPS.
- Tighten the bolts to the specified torque using a torque wrench.
- Recheck all connections and ensure they are secure.
After installing the new TPS, reset the engine control unit (ECU) by disconnecting the battery for a few minutes. This will allow the ECU to relearn the new TPS values.
Troubleshooting TPS Issues
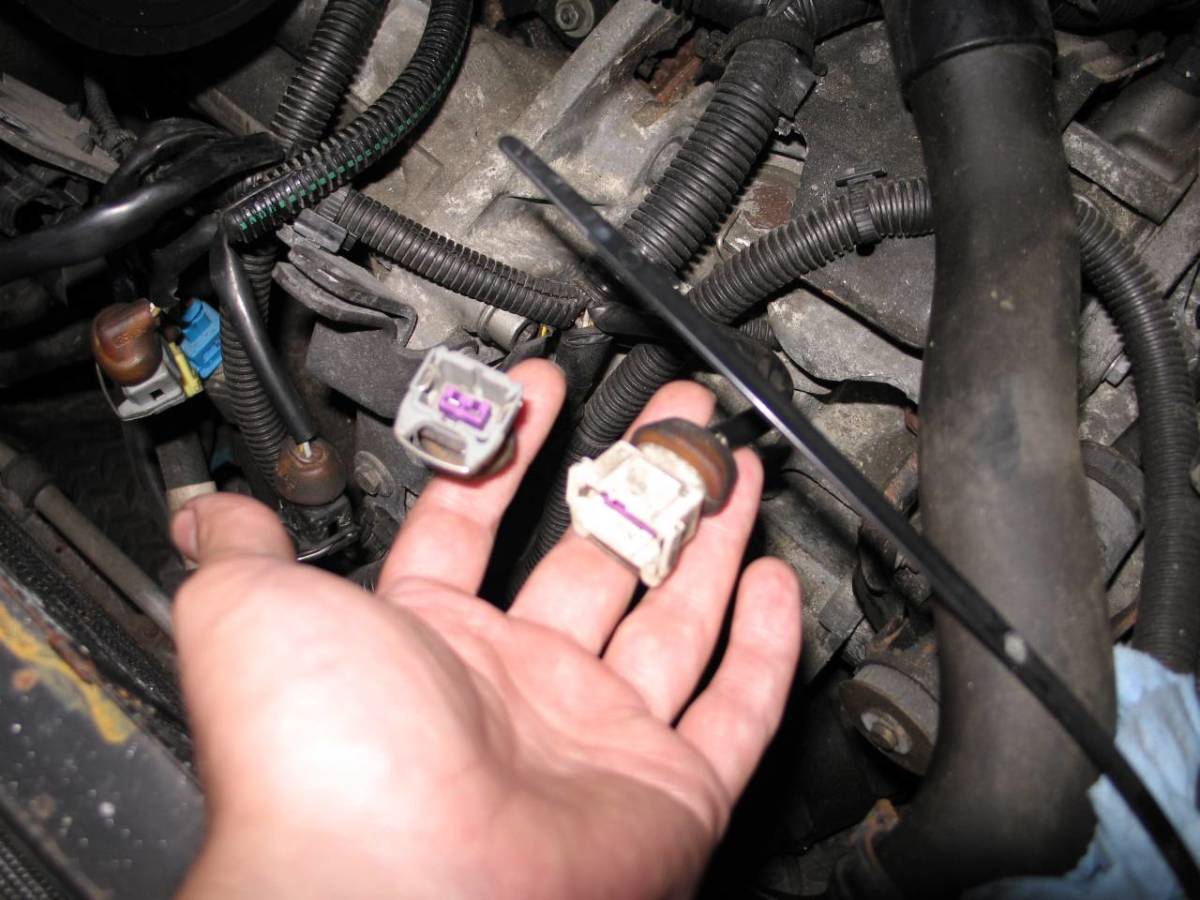

Identifying and resolving issues related to the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Various symptoms and diagnostic methods can help pinpoint TPS problems, enabling effective troubleshooting and repair.
Common Symptoms of a Faulty TPS
- Erratic engine idling or stalling
- Hesitation or surging during acceleration
- Poor fuel economy
- Check Engine Light (CEL) illumination
Methods for Diagnosing TPS Problems
- Visual Inspection:Check for any visible damage or loose connections to the TPS.
- Voltage Measurement:Use a multimeter to measure the voltage signal from the TPS at various throttle positions.
- Data Logging:Utilize a scan tool or data logger to record TPS readings during engine operation and identify any inconsistencies.
- Resistance Measurement:Measure the resistance between the TPS terminals with an ohmmeter.
Troubleshooting Tips for Resolving TPS-related Issues, Throttle position sensor location
- Clean the TPS:Carbon buildup or dirt can interfere with TPS operation. Clean the sensor with an appropriate solvent.
- Adjust the TPS:Incorrect TPS adjustment can cause performance issues. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper adjustment.
- Inspect Wiring:Check for any damaged or loose wires connecting the TPS to the engine control unit (ECU).
- Replace the TPS:If other troubleshooting methods fail, replacing the TPS may be necessary.
TPS Data Analysis and Interpretation
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) data plays a crucial role in modern engine management systems. By analyzing TPS data, engineers can gain insights into various engine parameters and optimize engine performance.
Methods for Analyzing TPS Data
There are several methods for analyzing TPS data, including:
- Time-domain analysis:This involves examining the TPS signal over time to identify patterns and trends.
- Frequency-domain analysis:This involves converting the TPS signal to the frequency domain using techniques like Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to identify dominant frequencies and harmonics.
- Statistical analysis:This involves using statistical techniques to determine the mean, variance, and other statistical parameters of the TPS signal.
TPS Data Interpretation in Different Driving Conditions
TPS data can be interpreted to provide insights into various driving conditions:
- Idle:TPS data near 0% indicates the engine is idling.
- Acceleration:Rapidly increasing TPS data indicates the driver is accelerating.
- Deceleration:Rapidly decreasing TPS data indicates the driver is decelerating.
- Cruise:Steady TPS data indicates the vehicle is cruising at a constant speed.
Last Recap
In conclusion, throttle position sensor location serves as a cornerstone in ensuring optimal engine performance. By understanding its function, identifying its placement, and addressing potential issues, individuals can effectively maintain and troubleshoot their vehicles, enhancing both safety and driving experience.
Essential Questionnaire
Where is the throttle position sensor typically located?
The throttle position sensor is usually mounted on the throttle body or carburetor, where it can monitor the position of the throttle valve.
What are the symptoms of a faulty throttle position sensor?
Symptoms of a faulty throttle position sensor can include rough idling, hesitation during acceleration, and poor fuel economy.
How do I troubleshoot a throttle position sensor?
To troubleshoot a throttle position sensor, you can use a multimeter to measure the voltage output of the sensor at different throttle positions.